Jenkins Setup in ubuntu
Step 1 — Installing Jenkins
First, add the repository key to the system:
wget -q -O - http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/debian/jenkins-ci.org.key | sudo apt-key add -
When the key is added, the system will return OK. Next, append the Debian package repository address to the server’s sources.list:
sudo sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
When both of these are in place, run update so that apt will use the new repository:
sudo apt update
Finally, install Jenkins and its dependencies:
sudo apt install jenkins
Now that Jenkins and its dependencies are in place, we’ll start the Jenkins server.
Step 2 — Starting Jenkins
Let’s start Jenkins using systemctl:
sudo systemctl start jenkins
Since systemctl doesn’t display output, you can use its status command to verify that Jenkins started successfully:
sudo systemctl status jenkins
If everything went well, the beginning of the output should show that the service is active and configured to start at boot:
Output
● jenkins.service - LSB: Start Jenkins at boot time
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/jenkins; generated)
Active: active (exited) since Mon 2018-07-09 17:22:08 UTC; 6min ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Tasks: 0 (limit: 1153)
CGroup: /system.slice/jenkins.service
Now that Jenkins is running, let’s adjust our firewall rules so that we can reach it from a web browser to complete the initial setup.
Step 3 — Opening the Firewall
By default, Jenkins runs on port 8080, so let’s open that port using ufw:
sudo ufw allow 8080
Check ufw’s status to confirm the new rules:
sudo ufw status
You will see that traffic is allowed to port 8080 from anywhere:
Output
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere
8080 ALLOW Anywhere
OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
8080 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Note: If the firewall is inactive, the following commands will allow OpenSSH and enable the firewall:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
sudo ufw enable
With Jenkins installed and our firewall configured, we can complete the initial setup.
Step 4 — Setting Up Jenkins
To set up your installation, visit Jenkins on its default port, 8080, using your server domain name or IP address: http://your_server_ip_or_domain:8080
In the terminal window, use the cat command to display the password:
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword Copy the 32-character alphanumeric password from the terminal and paste it into the Administrator password field, then click Continue.
The next screen presents the option of installing suggested plugins or selecting specific plugins:
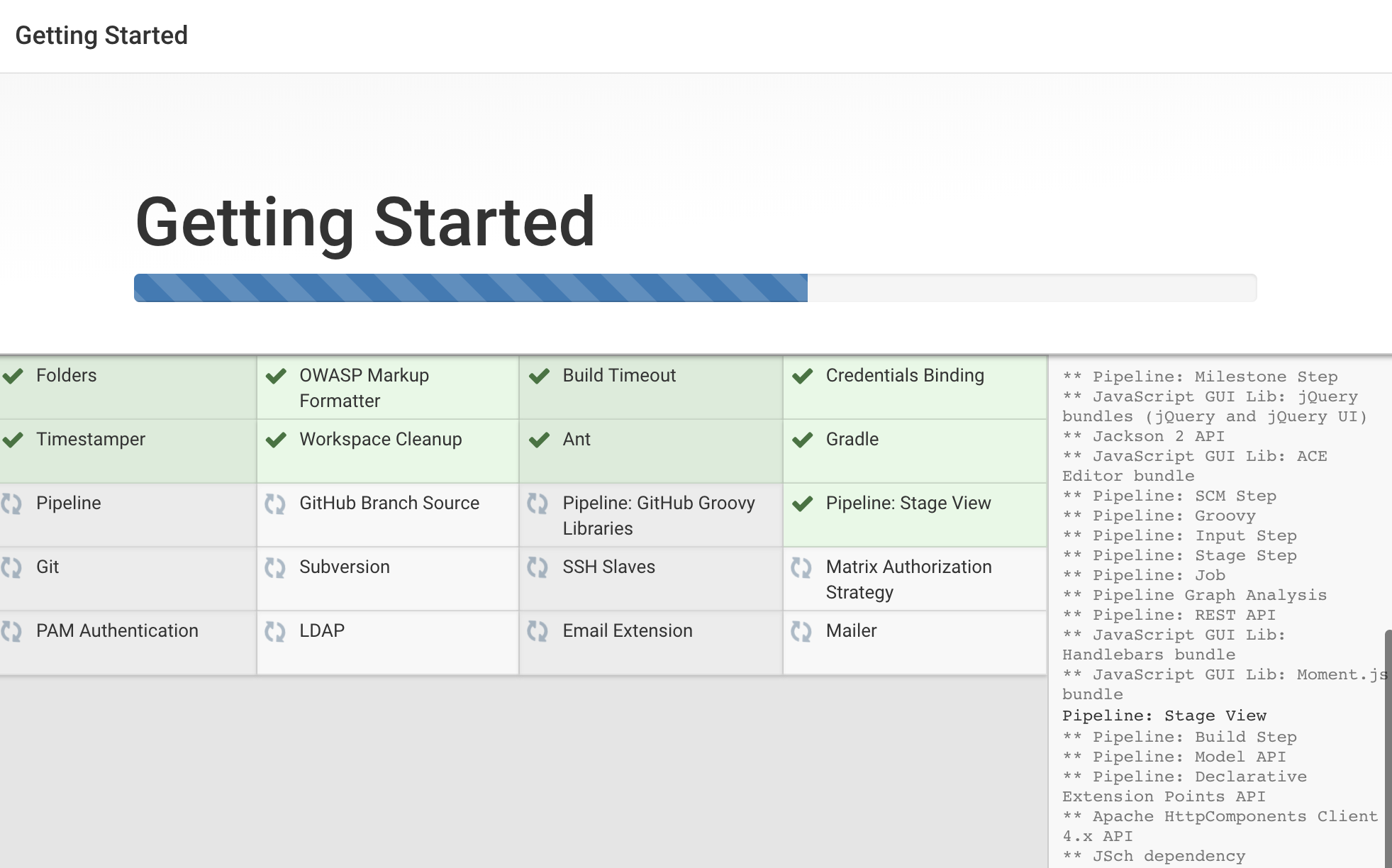
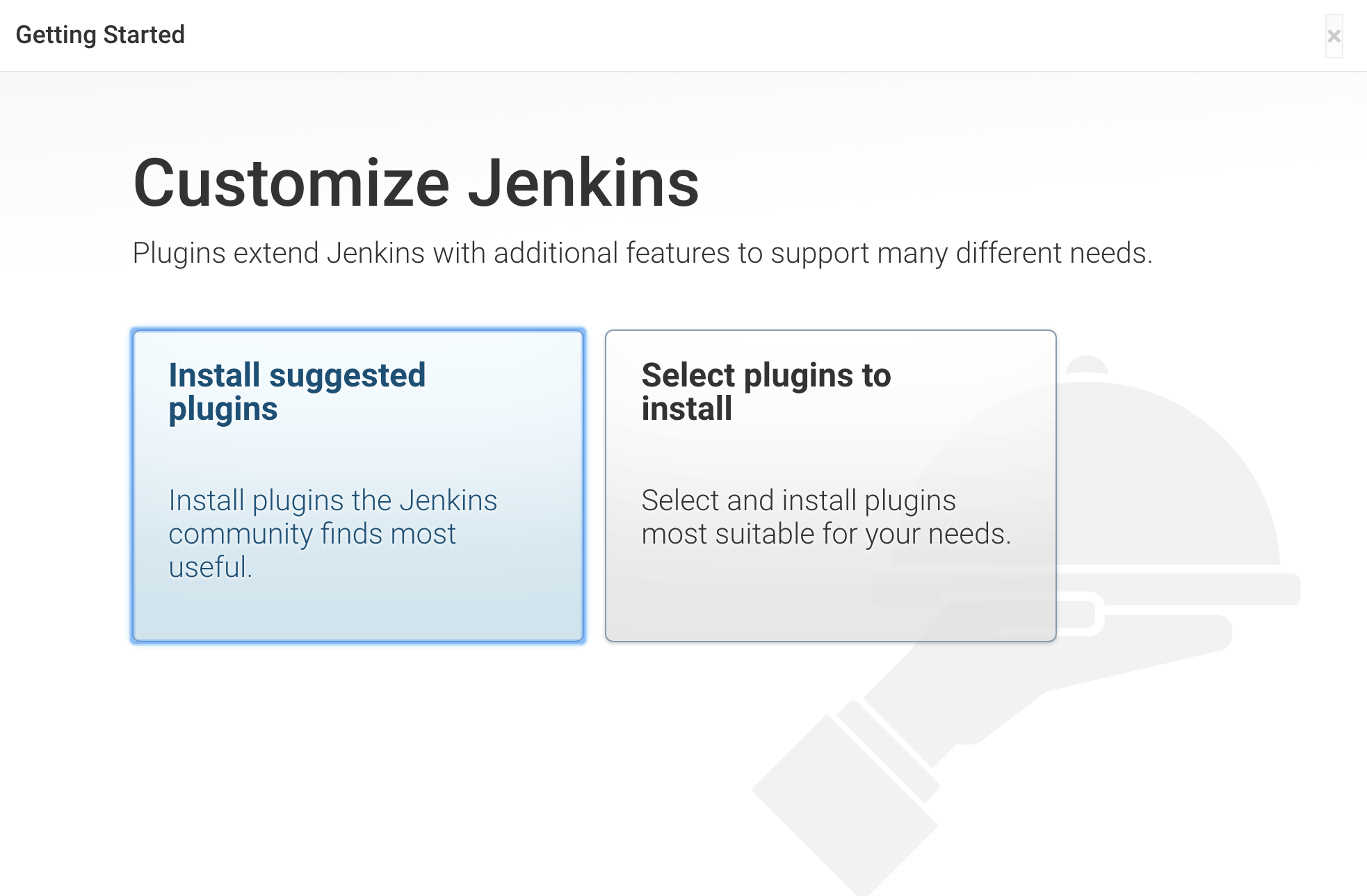 We’ll click the Install suggested plugins option, which will immediately begin the installation process:
We’ll click the Install suggested plugins option, which will immediately begin the installation process:
 continue as admin using the initial password we used above, but we’ll take a moment to create the user.
continue as admin using the initial password we used above, but we’ll take a moment to create the user.
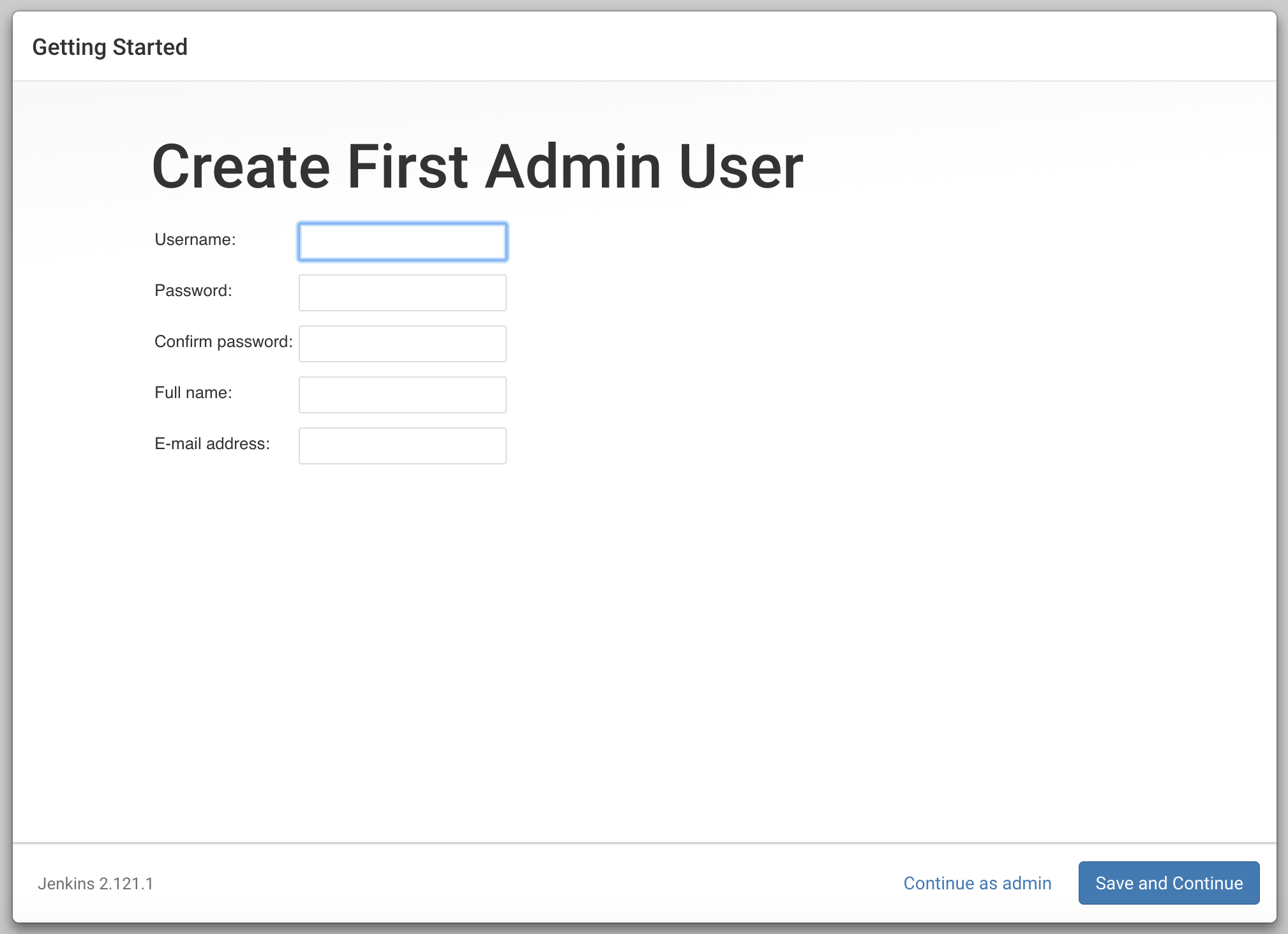 Enter the name and password for your user & click “save and continue” button twice.
Enter the name and password for your user & click “save and continue” button twice.
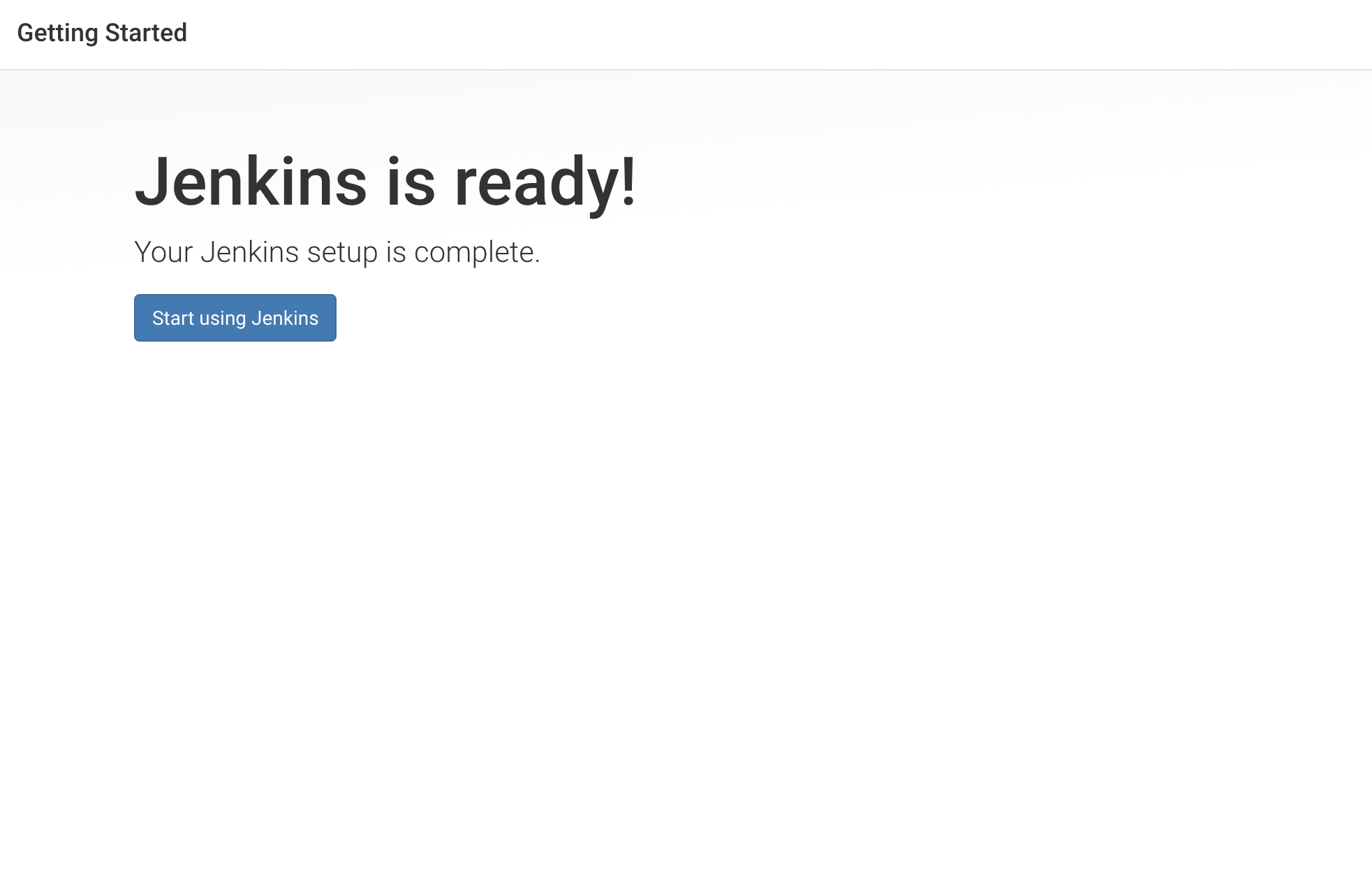 Click Start using Jenkins to visit the main Jenkins dashboard:
Click Start using Jenkins to visit the main Jenkins dashboard:
 At this point, you have completed a successful installation of Jenkins.
At this point, you have completed a successful installation of Jenkins.
Jenkins Change Running Port
in ubuntu,
sudo vi /etc/default/jenkins
Replace
HTTP_PORT=8080
with
HTTP_PORT=8086
Restart jenkins
sudo systemclt restart jenkins
& find jenkins is running on 8086 port. Thank you for reading this blog.